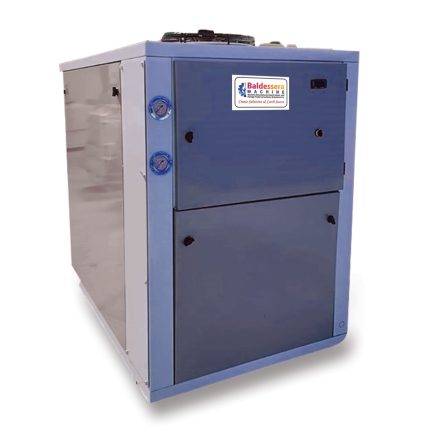
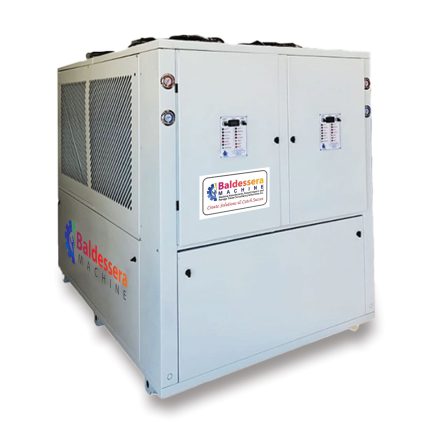
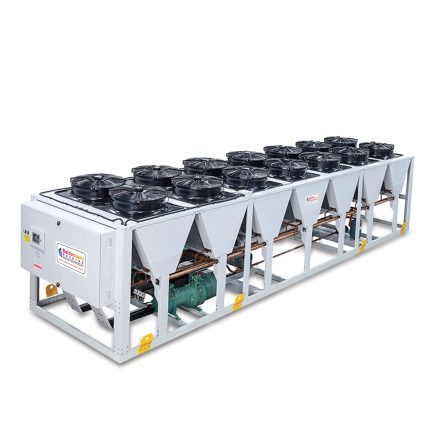
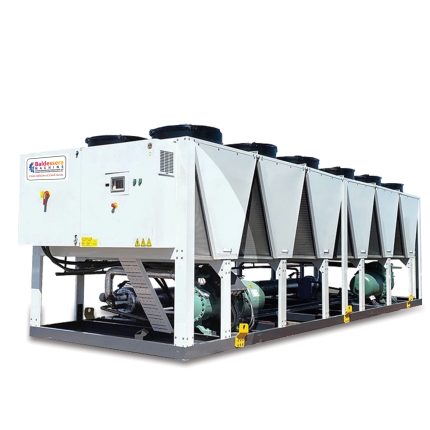
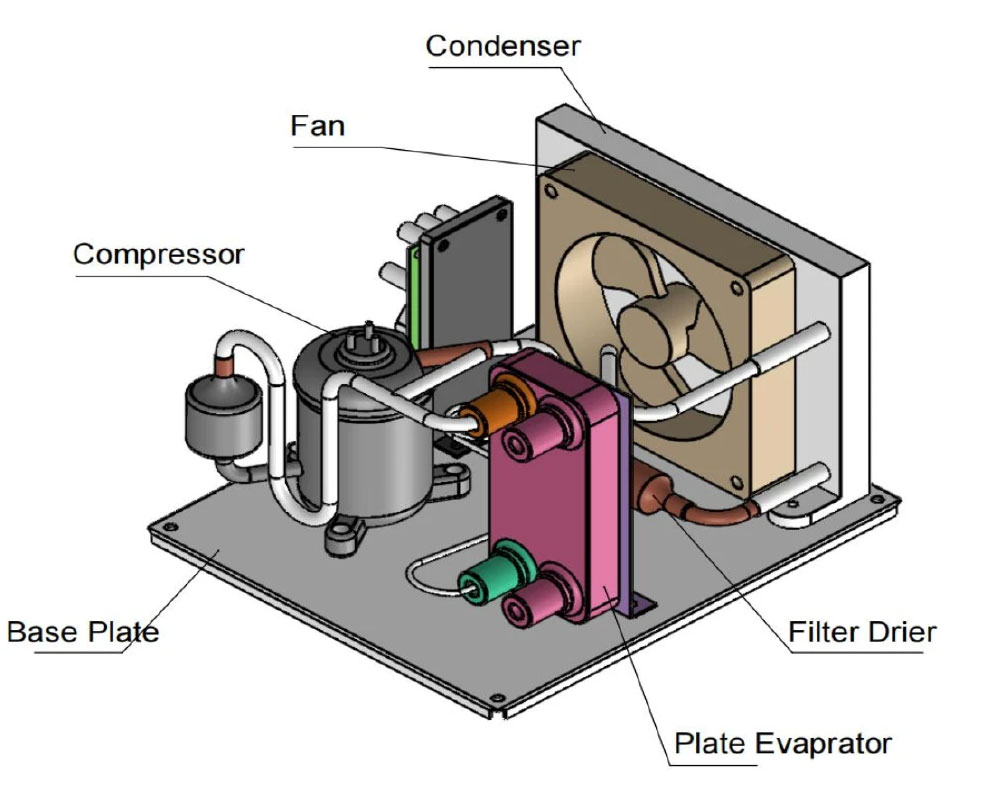
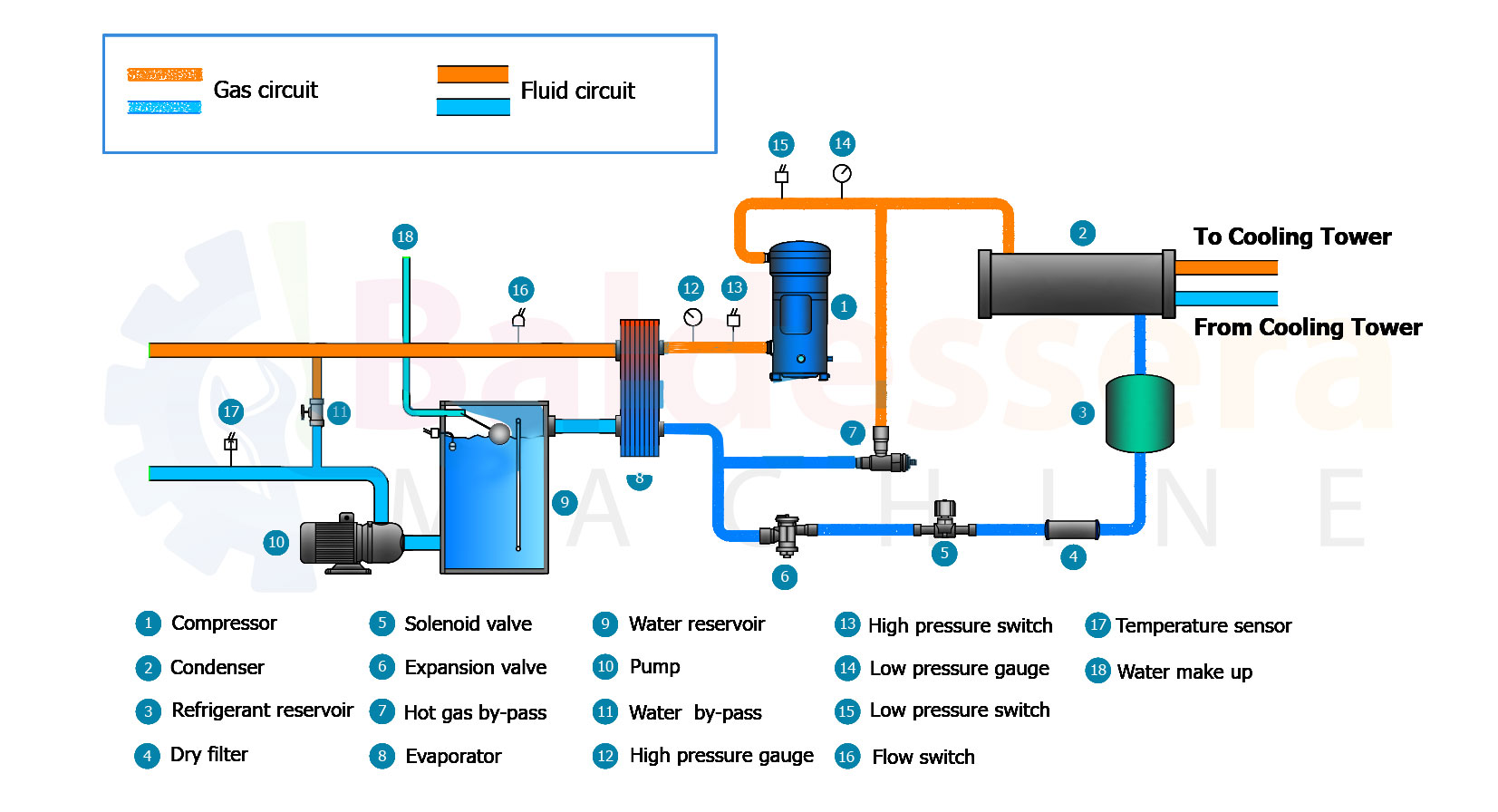
1. **Cooling Capacity**: Chillers are rated based on their cooling capacity, typically measured in BTU or kilowatts, to match the heat load of the welding machine.
2. **Temperature Control**: Many chillers come with thermostatic controls to maintain a specific temperature range, ensuring efficient cooling.
3. **Flow Rate**: A suitable flow rate is crucial for effective cooling. Chillers should be capable of circulating water at a rate sufficient to keep the machine cool.
4. **Compact Design**: Many modern chillers are designed to be space-efficient, fitting easily into production environments.
5. **Durability**: Built to withstand industrial environments, these chillers are often made from corrosion-resistant materials.
Benefits
- **Extended Equipment Life**: By maintaining optimal temperatures, chillers help prolong the life of welding machines and components.
- **Improved Weld Quality**: Consistent cooling ensures stable temperatures, leading to better weld quality and consistency.
- **Reduced Downtime**: Effective cooling minimizes the risk of overheating, reducing the need for maintenance and downtime.
Applications
- **Manufacturing**: Used in various industries, including automotive and electronics, where spot welding is prevalent.
- **Heavy-Duty Welding**: Essential for high-volume or heavy-duty welding applications that generate significant heat.
Considerations for Selection
1. **Compatibility**: Ensure the chiller is compatible with the specific spot welding machine in terms of connections and cooling requirements.
2. **Ambient Conditions**: Consider the environment where the chiller will be located, including temperature and humidity levels.
3. **Maintenance Requirements**: Look for chillers with
easy access for maintenance and service.
If you need more detailed information or
recommendations on specific models,
feel free to ask!