Alde Table Type Spot Welding Machine And How We
Can Use It For Metal Steel Door Manufacturing
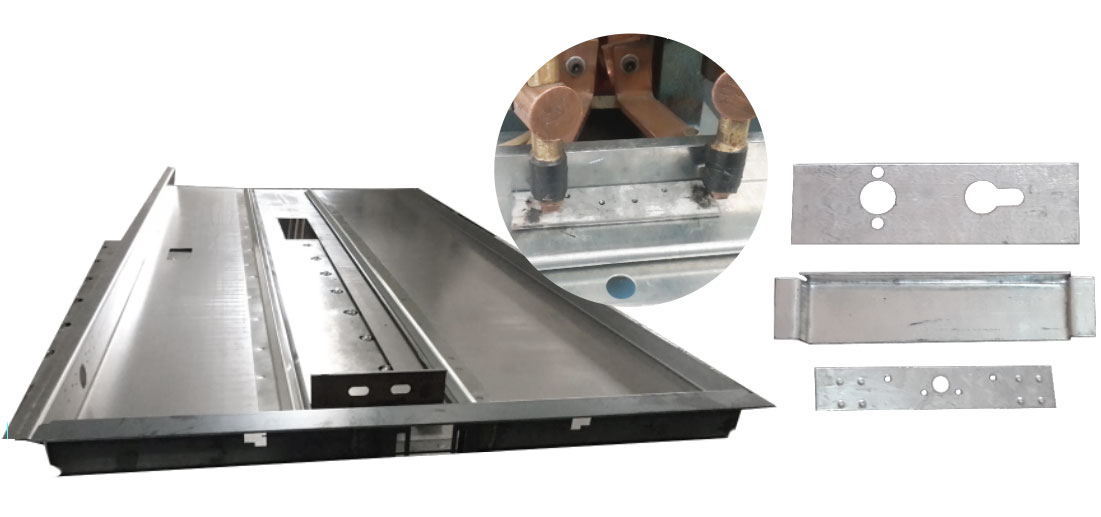
A table-type spot welding machine is a specific configuration of spot welding equipment designed for welding smaller components and assemblies that can be handled on a tabletop. Here are some key features
Components and Features
1. **Compact Design**: Ideal for applications with space constraints, the machine is designed to fit on a tabletop, allowing easy integration into workstations and assembly lines.
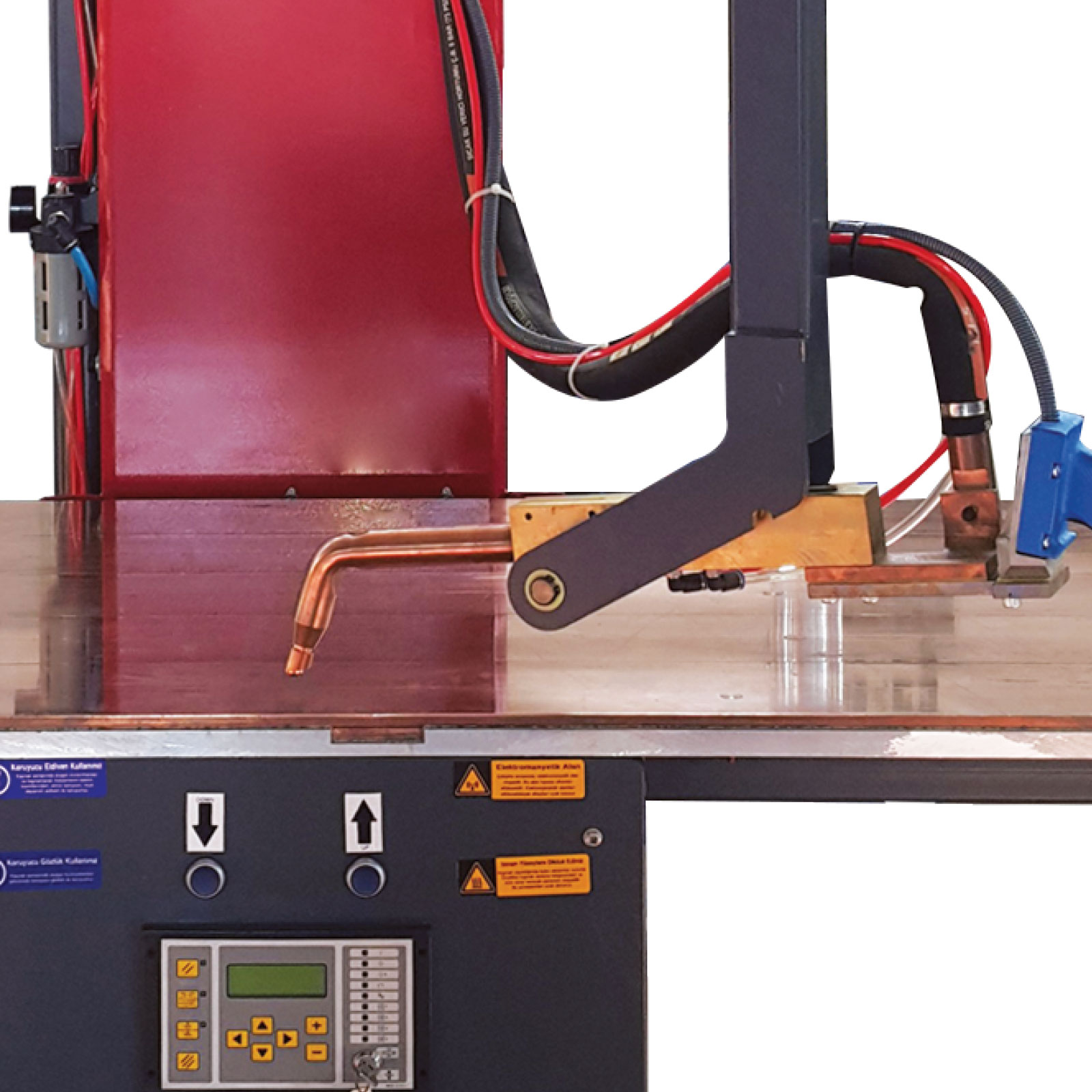
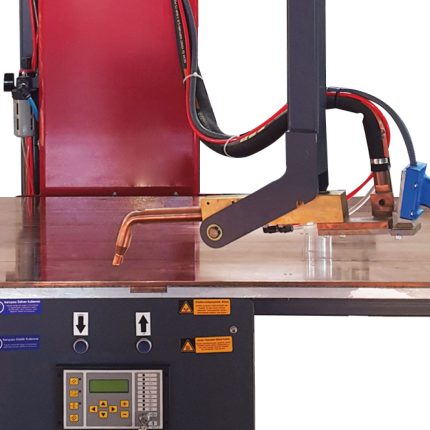
2. **Fixed Electrodes**: Usually, it has a fixed lower electrode on the table and an adjustable upper electrode (or vice versa) to accommodate varying material thicknesses and welding angles.
3. **Adjustable Weld Pressure**: Many machines offer adjustable pressure controls, enabling users to set the appropriate force based on material type and thickness.
4. **Electronic Control Systems**: Equipped with timers and current controllers to ensure consistent weld quality, making it easy to control weld times, currents, and intervals.
5. **Manual or Foot Pedal Operation**: Table-type machines often come with either a manual lever or a foot pedal, allowing the operator to initiate the welding process without using their hands directly.
Common Uses
- **Lightweight Sheet Metal Welding**: Commonly used for thin sheets and small parts in electronics, appliances, and other lightweight assemblies.
- **Automotive and Aerospace Parts**: Useful for welding small components in larger assemblies.
- **Jewelry and Precision Metalwork**: Often used for joining delicate metals due to its controlled settings.
Would you like to know more about a specific model or brand, or are you interested in seeing a setup example?
Using a table-type spot welding machine for metal steel door manufacturing is feasible but depends on the machine's capacity and the specific requirements of door construction. Here's how it could work and what you'd need to consider.
Application Scope
- **Smaller Components**: A table-type spot welder is most suited for smaller components of the door, like hinges, reinforcements, or smaller internal steel parts.
- **Thin Steel Sheets**: This machine is typically designed for thinner metal, so it would work well for welding door skins or panels, which are often thinner sheets of steel.
Steps in Manufacturing
- **Door Frame Assembly**: Smaller spot welders can help attach reinforcing metal bars or brackets to door frames.
- **Panel Attachment**: If the door has an inner and outer panel, the machine can spot-weld thin panels together at strategic points around the frame.
- **Reinforcement Components**: Weld reinforcing plates to specific areas (e.g., hinge or lock areas) for increased strength.
Welding Parameters
- **Pressure and Current Adjustment**: Since steel doors require firm joins, adjust the machine to a higher pressure and appropriate current. Test settings on sample pieces to avoid burn-through on thin panels.
- **Spacing and Weld Points**: Ensure even spacing for weld points to prevent panel warping and ensure strong adhesion, especially around door corners and edges.
Additional Considerations
**Heavy-Duty Table-Type Welder**: For steel doors, a more robust table-type spot welder with higher amperage is beneficial to handle thicker sections where required.
**Automation or Jigs**: Consider creating custom jigs or clamps to hold large panels in place on the table while welding, improving consistency and safety.
A standard table-type spot welder might need customization or upgrading to handle the thicker materials and larger sizes typical in metal door manufacturing, or you might need multiple machines for different stages. If you’re handling high volumes, an automated line with a robotic welder could also be a consideration for efficiency.